Tuesday, March 13, 2012
SAP Automotive Implementation in Sri Lanka
Sunday, March 11, 2012
SAP FI- TFIN50- Book 1- Unit 2 -Master Data
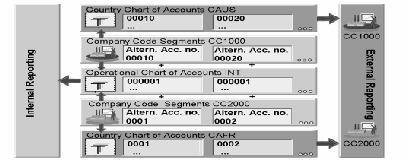
- Chart of accounts is a variant
- You define the chart of accounts with a four character ID.
- You define the individual components of the chart of account, for language, length of the G/L account number, group chart of accounts, status.
- The length of the G/L account numbers can be from 1 to 10 digits.
- If you enter a group chart of accounts in the chart of accounts, the system defines that you have to enter a group account number in the corresponding field in the G/L account definition.
- A chart of accounts that is not yet completed can be blocked so that no company code can use it until it is ready.
|

The Controlling component uses the same chart of accounts as the Financial Accounting component.
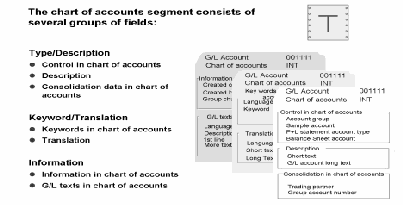
Chart of accounts segment contain:
- Account number
- Name of the account (as short and as long text)
- Control fields (see the following graphics)
- Consolidation fields
- If the chart of accounts has not been translated into the appropriate logon language, the account name appears in the maintenance language.
- You can search for account numbers using keywords.
- You can define and change the layout of the tab pages for the individual processing of the G/L account master data.
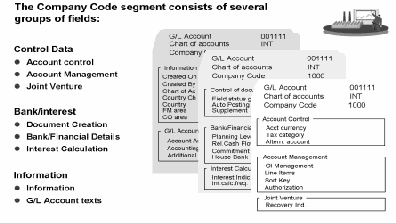
Company Code Segment
You define the information that is relevant to each company code:
- Currency
- Taxes
- Reconciliation account
- Line item display
- Sort key
- Field status group
- House bank
- Interest calculation information
You can display texts using the report .Account Assignment Manual.
Balance Sheet and P&L Statement Accounts
These two types of accounts are treated differently in the closing procedure.
- For balance sheet accounts, the balance is carried forward to the same account.
- For profit and loss statement accounts, the balance is carried forward to a retained earnings account and the profit and loss statement account is set to zero. A key (for example, X) is assigned to the account to which the balance is carried forward. You enter this key in the field "P&L Statement Type" in the chart of accounts segment.
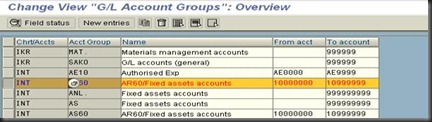
Account Group
By assigning a number range to an account group, you can ensure that accounts of the same type are within the same number range. Number intervals for G/L account master records can overlap.
You must enter the account group in the chart of accounts segment.
· The field status enables you to control the display and maintenance of an account's master data.
· Certain fields are grouped together and their field status is valid for the entire group, for example, interest calculation indicator, interest cycle, and last interest calculation key date.
· The fields Account Currency and Field Status Group are always required fields. This status cannot be changed.
· Fields that are hidden may still contain values that are taken into consideration.
Priority in the field status
- Hide
- Display
- Required entry
- Optional entry
Reconciliation Accounts - general ledger accounts assigned to the business partner master records to record all transactions in the sub-ledger.
You define a G/L-account as a reconciliation account by entering one of the following account types in the field Reconciliation Account for Account Type:
- D for Accounts Receivable
- K for Accounts Payable
You cannot post amounts directly to reconciliation accounts.
If you want to look at the business partner accounts (customer / vendor) assigned to a specific reconciliation account, you can select the field for the reconciliation account in the customer or vendor list (RFDKVZ00 or RFKKZV00) via the free selections.
Line Item Display
The .Line Item Display field is a control field in the company code segment of an account.
You can use report RFSEPA01 to subsequently activate the line item display - read the documentation for this report before you execute it.
You should not activate the line item display for:
- Reconciliation accounts
- Revenue accounts
- Material stock accounts
- Tax accounts
Open Item Management
Accounts with open item management must have line item display activated.
Open item management is a prerequisite if you need to check whether there is an offsetting posting for a given business transaction.
You should use open item management for the following accounts:
- Bank clearing accounts
- Clearing accounts for goods receipt/invoice receipt
- Salary clearing accounts.
You can only activate or deactivate open item management if the account has a zero balance.
Account in Local Currency
You can select one of the following currencies as account currency:
- Local currency
- Foreign currency
If the account currency is the local currency, the account can be posted to in any currency.
This applies whether or not line item display is activated.
Only Balances in Local Currency
Only Balances in Local Currency" checkbox is set in the master data record, transaction figures are only managed for amounts converted to the local currency.
You should select this field for clearing accounts where you want to clear accounts by assigning items with the same local currency amount with one another, without necessitating exchange rate difference postings.
The indicator must be set in cash discount and GR/IR clearing accounts.
It must not be set in reconciliation accounts for customers or vendors.
The indicator is usually set in balance sheet accounts that are not managed in Foreign currencies and not managed on an open item basis.
Accounts with a foreign currency as the account currency can only be posted to in this foreign currency.
G/L Account creation
- Create manually ( in two steps )
- Create G/L account by coping
- Date transfer (To reduce data entry, programs such as RFBISA00, Batch Input
Interfaces )
Group Chart of Accounts
The group chart of accounts must be assigned to each operational chart of accounts. After you have done this, the .Group Account Number. Field in the chart of account segments of the operational charts of accounts becomes a required entry field.
You must use a financial statement version for the group chart of accounts.
Because the company codes use different operational charts of accounts, you cannot carry out cross-company code controlling.
Country Chart of Accounts
The country chart of accounts number (alternative account number) is entered in every company code segment.
Since all company codes use the same operational chart of accounts for postings, you can carry out cross-company code controlling.
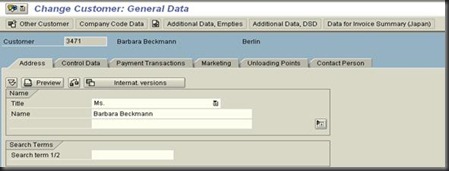
Customer / Vendor Accounts
Customer vendor account segments:
- One segment at client level that contains general data. This data can be accessed throughout the whole organization.
- A segment at company code level that contains company code-specific data.
Using reports RFBIDE10/RFBIKR10, you can transfer customer/vendor master data maintained in a source company code into another company code.
Any sales area that wants to do business with a customer has to create a sales area segment first. The sales area segment contains sales area-specific data.
Any purchasing organization that wants to do business with a vendor has to create a purchasing organization segment first
A complete customer account consists of the following three segments:
- General data at the client level
- Company code segment
- Sales area segment
Can prevent the creation of duplicate accounts as follows:
- Use the match code before you create a new account
- Activate the automatic duplication check
Important fields are:
1. Search terms: You can enter an abbreviation for the customer/vendor name in these fields.
2. Corporate Group: Customers or vendors who belong to one corporate group can be grouped together by a user-defined group key. This group key can be used for running reports, transaction processing, or for match codes.
3. Accounting clerk: The name of the accounting clerk must be saved under an ID.
Line item display and open item management are configured as standard for every
Customer/vendor account.
· The IBAN contains a maximum of 34 alphanumeric characters and is structured differently in every country. (It usually contains the country code, bank key, and account number.)
When you enter an IBAN for new bank details, the system can generate the country-specific bank details for certain countries.
In Financial Accounting, once the customer/vendor account has been created, you can no longer change the account group.
Customer / vendor Number ranges must not overlap. Each number range can be assigned to one or more account groups.
You enter the customer-/vendor-specific data for one-time customers/vendors in the document during posting.
The layout of customer/vendor master data screens can be affected by several factors:
Account group-specific control – field status
Transaction-specific control - The transaction-dependent field status should be set to display for the .change. transaction if the field is not to be changed after it has been created, such as the .reconciliation account.
field, for example
Company code-specific control - You can control the field status for fields in the company code
segment of customer and vendor master records
If you do not want to use the transaction-specific or company code-specific control, set the field status for all fields to optional. Since this field status has the lowest priority, the account group-specific control is always used.
Dual control principle
If you define a field in the customer/vendor master record as .sensitive., the
corresponding customer/vendor is blocked for payment if the entry is changed.
Customer/Vendor Clearing
- If a customer is also a vendor, or vice versa, the payment and the dunning program
can clear open items against each other
- If you set the indicator Account Control and Status in the area Additional Selections in the report for the customer or vendor list when you print the report you can see the partner relationships for the respective customer or vendor.
Alternative Payer/Payee
At the client and company code level, you can enter an alternative payer/payee. The entry in the company code segment has higher priority than the entry at client
level.
- If Alternative payer / payee is not a existing customer
If alternative payer/payee is an existing customer or vendor
Head Office/Branch
All items posted to a branch account are automatically transferred to the head office account.
Usually, dunning notices go to the head office and it is the head office that makes and receives payments.
if the Decentralized Processing field is selected in the head office master record, the dunning and payment programs use the branch account instead.
Bank Accounts
Every bank that is used in the system you have to create a bank master record.
Bank master records are stored centrally in the bank directory (table BNKA)
Every record is identified by the bank country and the bank key
Banks that your company uses are defined as house banks.
House bank contain
Bank master data, information for electronic payment transactions, bank accounts per house bank, and general ledger accounts per bank account.
Payment program uses the house bank ID and the bank types to determine the bank to be used
Bank master data can be created four ways:
- When entering bank information in the customer or vendor master record
- Using the Create Bank transaction in the Accounts Receivable/Payable ( FI03 )
- The bank directory can be imported from disk or tape using program RFBVALL_0, Country-Specific Transfer of Bank Data.
- Customers that use the lockbox function can create a batch input session that automatically updates customer banking information in the master record.
In the customer/vendor master record, the field “Bank Type” is used to distinguish between different banks.
When processing invoices, if the customer/vendor has more than one bank, the user can choose a bank by using the match code in the partner bank field.
Each bank account is reflected in the SAP ERP system by a combination of house bank ID and account ID. This combination is entered in a G/L account that represents the bank account in the general ledger
The accounts can be identified by an account ID which is unique per house bank.
The bank account data contains the number of the account at your bank, the account currency, and the relevant G/L account.
For every bank account, a G/L account must be created. Both accounts have to have the same account currency.
True or false?
1. Reconciliation accounts are updated on a daily basis.
Answer: False
The reconciliation accounts are updated real time.
2. You can always display the line items of a G/L account.
Answer: False
You can only display the line items if the account is managed with line item display.
3. G/L accounts with open item management must have line item display
Answer: True
You cannot define a G/L account with open item management without selecting the Line item display option.
4. G/L accounts that are managed in local currency can only be posted to in this currency.
Answer: False
G/L accounts in local currency can be posted to in any currency.
5. G/L accounts that are managed in a foreign currency can only be posted to in this foreign currency.
Answer: True
If you select a foreign currency as the account currency, you can only post amounts in this foreign currency to this account.
6. Because the company codes use different operational charts of accounts, you cannot carry out cross-company code controlling.
Answer: True
You can carry out cross-company code controlling if each company code uses the same operational chart of accounts.
1. The customer/vendor accounts must always be maintained centrally.
Answer: False
Customer/vendor accounts can be maintained centrally or decentrally.
2. One number range can only be assigned to one account group.
Answer: False
A number range can be assigned to several account groups.
Saturday, March 10, 2012
SAP FI–TFIN50 - Book 1 - Unit 1- Organizational Units
Organizational Units in my SAP ERP Financials
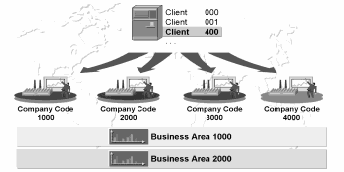
The use of business areas is optional.
Each client is an independent unit with separate master records and a complete set of tables and data.
You have to select a four digit alphanumeric key as the company code key.
When you define a business area, you only have to enter a four digit alphanumeric key and a short description.
> If you need a company code for a country that has a country template, you can use the country installation program to copy the country-specific tables from the country template to company code 0001.
> The country installation program not only creates a country-specific company code template but also a country-specific template for controlling areas, plants, purchasing organizations, sales organizations, credit control areas, financial management areas, and so on.
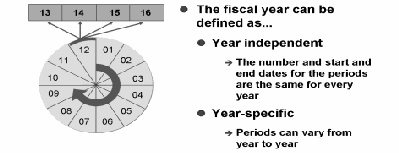
Fiscal year variant
To assign business transactions to different periods, you have to define a fiscal year with posting periods
The fiscal year variant contains the definition of posting periods and special periods.
- In total, you can define 16 periods.
- If the posting date falls within the last normal posting period, you can post the transaction in one of the special periods.
- The fiscal year variant does not specify whether a period is open or closed. This data is managed in another table. The fiscal year variant only defines the number of periods and their start and finish dates.
Year-Independent Fiscal Year Variant
Each fiscal year of a fiscal year variant uses the same number of periods, and the posting periods always start and end on the same day of the year,- year-independent
- A non-calendar year can have between 1 and 16 posting periods.
- Fiscal years are normally year-independent.
Non – calendar year – (Year shift)
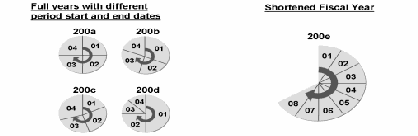
Year-Specific Fiscal Year Variants
- The start and end dates of the posting periods for some fiscal years are different to the dates for other fiscal years.
- Some fiscal years use a different number of posting periods.
- If one year of a fiscal year variant has less posting periods than the others, it is called a shortened fiscal year
Currencies
- A currency key must be assigned to every currency used. Each currency key can have a validity date.
- These different exchange rates can be used for various purposes such as valuation, conversion, translation, and planning.
| |||||
| |||||
| |||||
Translation Ratios
Base Currency
You can use more than one base currency per exchange rate type.
|
|
|

|
|
| ||||||
Tools use to maintaining exchange rates:
- Inversion (of the tools available, inversion is the oldest and is seldom used today)
- Base currency
- Exchange rate spreads
Transfer external market data - You can automatically update the exchange rate table by uploading an input file in Multicash form.
Transferred real-time exchange rate using a data feed interface - Remote Function Call (RFC) creates a direct connection between an external system and the SAP.
Efficient combination of the exchange rate tools is:
- Using a base currency for the average rate (M)
- Using the exchange rate spreads to calculate the buying and selling rates (B and G)
Direct/Indirect Quotation of Exchange Rates
- The use of indirect quotation is neither application nor country-specific - it affects all the components in which exchange rates are used.
- In direct quotation, one unit of foreign currency is quoted for the local currency, whereas in indirect quotation, one unit of local currency is quoted for the foreign currency.
Direct quotation - One unit of foreign currency USD costs the displayed number of units of local currency
Indirect quotation - For one unit of the local currency EUR you will receive the displayed number of units of the foreign currency.
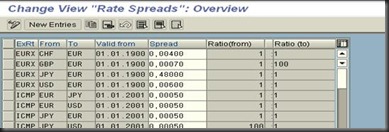
Exchange rate spared
Work list to update Exchange rate:
With work list following can be achieved:
- Only the relevant exchange rates can be maintained. You can also assign authorizations for work lists.
- Only the relevant quotation can be maintained.
- The work list is smaller and therefore clearer.
- Parallel processing of different work lists is possible.
Design of exchange rate in different quotations
- (blank, without a prefix) * for direct quotation exchange rates
- ./. for indirect quotation exchange rates
True or false?
1. You can assign a business area to a company code directly.
Answer: False
Business areas are not directly assigned to company codes. This makes it Possible to evaluate transaction figures for each business area beyond the boundaries of the company code too.
First steps in Fiori launchpad – User Guide
With new S/4 HANA, users get a new user experience with Fiori apps. This document covers few useful tips on Fiori launchpad tile m...

-
With new S/4 HANA, users get a new user experience with Fiori apps. This document covers few useful tips on Fiori launchpad tile m...
-
Chart of accounts is a variant You define the chart of accounts with a four character ID. You define the individual components of the c...